

What is a Brain Aneurysm
and an AVM?
A brain aneurysm is an abnormal bulge or "ballooning" in the wall of an artery in the brain. A brain aneurysm can leak or rupture, causing bleeding into the brain resulting in a hemorrhagic stroke. A hemorrhagic stroke is either a ruptured brain aneurysm or a weakened blood vessel that leaks which suddenly interferes with the brain's function. Blood spills into or around the brain which creates swelling and pressure, damaging cells and brain tissue.


An AVM is an Arteriovenous Malformation which is an abnormal and weak blood vessel wall that connects an artery and a vein. This weak vessel is present from birth and is larger than a capillary so blood that flows in can be at high pressure, eventually causing the AVM to stretch and leak.
Normally, arteries take blood from the heart to the body. Blood then is brought through the arteries into capillaries and then into the veins. Capillaries are tiny vessels and helps the blood to slow down. In an AVM there are no capillaries, so blood does not slow down and doesn't get to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the body's tissues.
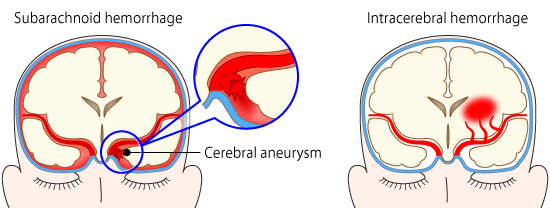
There are two types of hemorrhagic strokes:
Subarachnoid hemorrhage- During a hemorrhage, the subarachnoid space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid, causing that space to become bloody. As blood flows into the cerebral spinal fluid, it increases pressure on the brain, resulting in an immediate
headache. Most of the time this is due to a leaking Saccular aneurysm but it can occur as the result of a leaking AVM.
Intracerebral hemorrhage - Bleeding occurs from a broken blood vessel within the brain. The bleeding causes brain cells to die and the affected part of the brain stops working correctly. In some cases, this may occur because of a leaking AVM.
When an aneurysm ruptures even though the bleeding may only last for seconds the blood can damage or destroy brain cells. A condition called Vasospasm can occur if bleeding causes the arteries to narrow. This reduces the flow of blood to vital areas of the brain. This in turn can result in the patient having an ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction). This will in turn cause the brain tissue to die due to the lack of blood.
Hydrocephalus can take place if there is a large amount of blood in the spinal fluid. This results in a buildup of fluid in the cavities of the brain causing pressure on the brain tissue which can result in brain damage.
Someone that has suffered a rupture may have temporary or permanent deficits such as problems with vision, speech, memory, thinking, fatigue, balance and coordination.